Complete Basics of CNC Machining Technology for Beginners
Do you want to learn the basics of CNC machining and its role in manufacturing? Computer numerical control (CNC) machining is a key part of modern manufacturing, using advanced machine tools to precisely cut and shape a wide variety of parts.
This article provides an in-depth overview of CNC technology, the basic working principles of CNC machines, and their applications across various industries. It also explains why this technology is essential in modern manufacturing.

What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a computer-controlled manufacturing process used to produce high-precision parts. In this process, a computer program controls the movement of cutting tools to remove material from a workpiece and create a finished part.
CNC machining can produce a wide variety of parts made from materials such as metal, plastic, and composites. It is capable of creating complex geometries with high precision, making it a popular manufacturing method across many industries.
Compared with traditional machining methods, CNC machining offers higher accuracy, better consistency, and greater efficiency. It also enables the use of advanced cutting tools and techniques, such as multi-axis machining centers and high-speed machining, which further improve machining quality and productivity.
History of CNC Machining
The history of CNC machining dates back to the 1940s and 1950s, when the first numerically controlled (NC) machine tools were developed. Over time, these machines became more common and increasingly sophisticated, allowing them to meet the needs of a wide range of industries. However, early NC and CNC systems still required significant manual intervention and had limited functionality.
A major transformation in manufacturing technology occurred in the 1970s, when the introduction of computers led to a breakthrough: the development of computer numerical control (CNC) machine tools. These machines were equipped with computer-based control systems capable of processing data with much greater speed and accuracy. This innovation allowed operators to input programs directly into the machine, which could then automatically execute machining operations, greatly improving efficiency and consistency.
This marked the beginning of modern CNC machining. Over the years, advances in software, hardware, cutting tools, and materials have continued to expand the capabilities of CNC machines. Today, CNC machining is widely used across multiple industries to produce a broad range of products with high accuracy and precision..
How does CNC machining work?
Modern CNC systems are designed to minimize human intervention, ensuring consistent performance and reliable results. This high level of automation supports smart manufacturing and improves overall production quality. However, successful CNC machining requires careful planning from the initial design stage to final production. The entire CNC machining process can be divided into three main steps.
Step 1: Design
The first step in CNC machining involves the use of software tools such as CAD (Computer-Aided Design), CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing), and CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering). Engineers and designers use these tools to create part designs and evaluate their manufacturability. This evaluation process, known as Design for Manufacturing (DFM), is critical because it helps optimize designs, improve efficiency, and reduce production costs while considering the limitations of machining processes.
In many cases, CAD models are prepared for manufacturing using CAM software, which may be integrated into the CAD platform or used as a separate application. Once the design is finalized, it is converted into a CNC-compatible file format, most commonly STEP or IGES, for further processing.
Step 2: Preprocessing and Programming
In this step, the design is turned into instructions that tell the CNC machine what to do. These instructions are called CNC programs. They control how the cutting tools move, how fast they spin, and how the machine operates.
Most of this work is done using special software, so the operator usually does not need to write the instructions by hand. Simple parts can be programmed very quickly, while more complex parts take more time to prepare and check. If the design is reasonable, the machining process will be smoother and more reliable.
Step 3: Machining
The final step is the actual machining. The CNC machine follows the program and cuts away extra material from the raw block to create the final part. During this process, high accuracy is very important, but it is difficult to make a part exactly the same as the computer model.
For this reason, manufacturers allow small differences in size, called tolerances. Different industries allow different tolerances. In general, the tighter the tolerance, the more time, effort, and cost are required to produce the part.
Common Types of CNC Machining
CNC machining includes different processes, and the type used depends on the shape, size, and accuracy required for a part. Simple parts may need only one machining process, while more complex parts often require several different operations. Below are some of the most common CNC machining methods used in manufacturing.
CNC Milling
CNC milling is a high-precision, versatile machining process used to remove material from a solid block to form a specific shape or design. It requires the use of a CNC system to control a multi-point cutting tool (usually a milling cutter) with extremely high precision. During this process, the workpiece is firmly mounted on the table and the milling cutter rotates at high speed to systematically remove material. This method is particularly suitable for machining flat surfaces, but its application range goes far beyond simple shapes.
One of the main features of CNC milling machines is the ability to perform intermittent cutting through multiple machining steps to efficiently create complex geometries. The technology has evolved to include 3-axis, 4-axis, and 5-axis milling machines:
- 3 axis milling: With movement along the X, Y, and Z axes, basic operations such as drilling and planing can be achieved. This method is ideal for simple projects that require simple shapes and is popular for its simplicity. However, it has limitations in creating complex geometries, making it more suitable for less complex designs.
- 4 axis milling: With the addition of a rotary axis, more complex operations can be achieved than 3-axis milling. This method is ideal for angled cuts and more complex shapes, expanding the capabilities of CNC machining. It is particularly useful for parts that require a higher level of precision that a 3-axis milling machine cannot provide.
- 5 axis milling: This machining method is the pinnacle of CNC milling, moving along five axes simultaneously, allowing for extreme precision and complexity. In high-precision industries, it is essential for creating workpieces with tight tolerances and complex shapes. This method streamlines the production process by reducing the need for multiple setups, ensuring efficiency and accuracy.
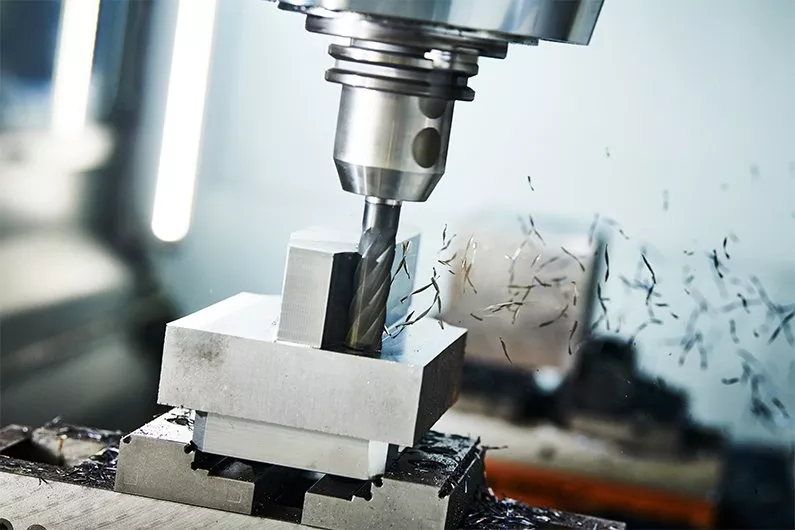

CNC Turning
CNC turning technology is a highly efficient machining process that is primarily used to shape cylindrical workpieces, but is also suitable for processing square or hexagonal raw materials. The core of CNC turning is the use of a computer-controlled lathe to rotate the workpiece using a variety of cutting tools. These tools trim and shape the material into the desired cylindrical shape. The uniqueness of the lathe lies in its versatility and high precision, which is controlled by different spindles and speeds. The process can be performed in both vertical and horizontal settings, each of which is suitable for specific types of workpieces and machining requirements. There are two main types of machines in CNC lathe equipment:
- CNC lathe: It excels in precision turning operations and is well suited to machining high-precision cylindrical parts. It operates by rotating the workpiece relative to a fixed tool, which is ideal for machining simple to moderately complex shapes and is commonly used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
- CNC turning center: It combines turning with additional functions such as milling and drilling. This multitasking ability allows complex parts to be produced in a single setup, thereby improving efficiency and precision. It is essential for industries that require complex, multi-faceted components, such as advanced manufacturing.
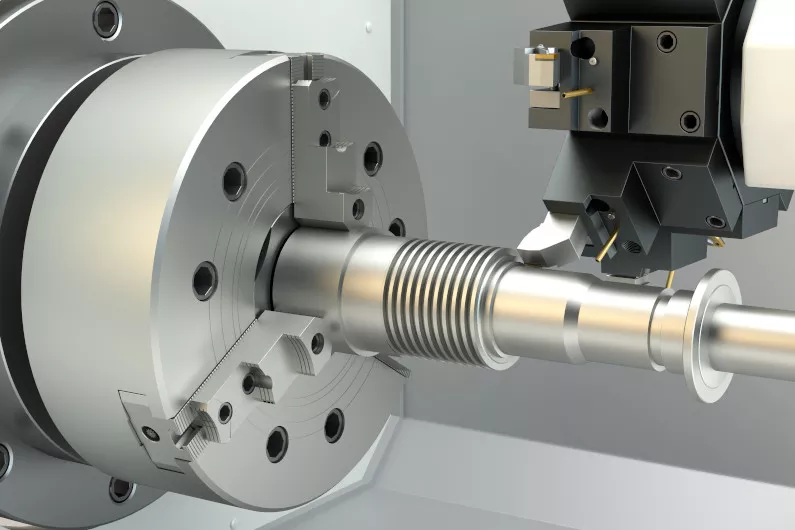
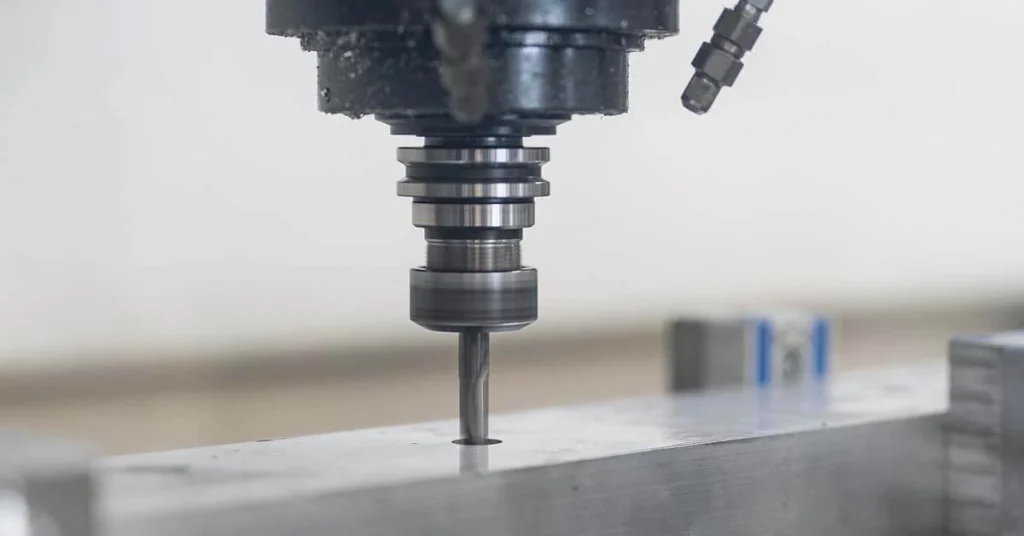
CNC Drilling
CNC drilling is used to create holes in a workpiece. The machine precisely controls the position, speed, and depth of the drill. After drilling, holes can be further processed, such as tapping, to create threaded holes. CNC drilling is widely used in industries such as electronics, metal fabrication, and plastics manufacturing.

CNC Routing
CNC routing works in a similar way to CNC milling but is mainly used for softer materials such as wood, plastic, and composites. CNC routers typically operate at higher speeds and are commonly used in furniture making, signage, and panel cutting. Like other CNC machines, routers offer good accuracy, repeatability, and efficiency.

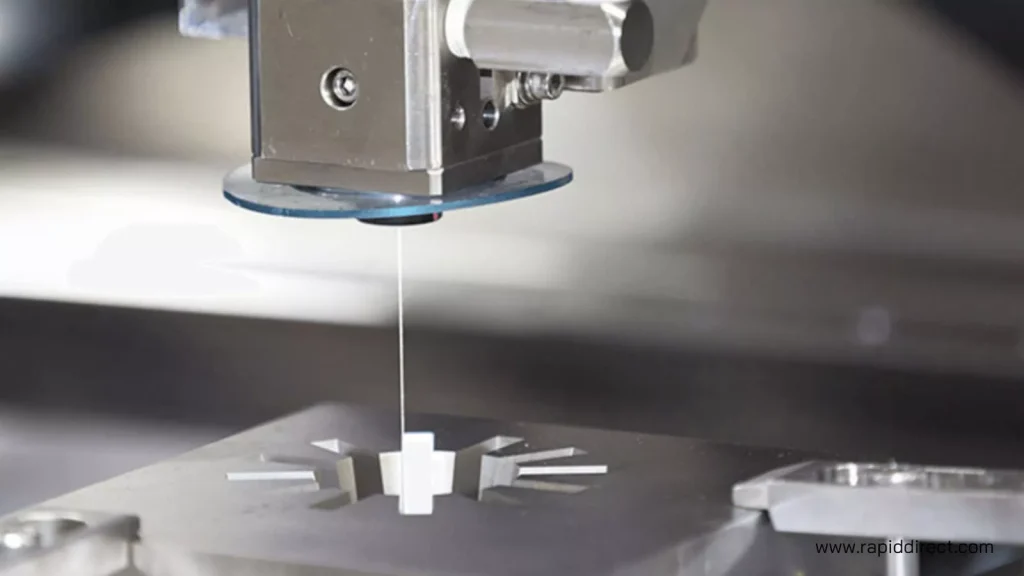
Electrospark machining
Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is a manufacturing process that uses electrical discharge to erode material and produce complex shapes and geometries. The process works by creating a spark between an electrode and a workpiece. The machinist immerses the workpiece in a dielectric fluid that isolates the electrical energy and allows for precise control of the spark. The spark discharge vaporizes the workpiece and removes excess material to achieve the desired shape. There are two main types of EDM: sinker EDM and wire-cut EDM. Sinker EDM uses a consumable electrode to produce the spark. Wire-cut EDM, on the other hand, uses a thin metal wire that moves back and forth to produce the spark.

Different types of CNC machines
The capabilities of CNC machines vary widely, influenced by their complexity and cost. Some machines are versatile and can perform a variety of operations, while others are specialized for specific tasks. Here are the most common types of CNC machines in the industry:
- 3-, 4-, and 5-axis milling machines: These machines perform complex material removal using a variety of tools, including lathes and waterjets. Operating across multiple axes (horizontal, vertical, and tilted), these machines are capable of fine milling of wood, metal, and plastic, increasing efficiency by minimizing material repositioning.
- Lathes: The turning process involves holding the material on a rotating mechanism, usually a lathe. As the material rotates, CNC tools remove small amounts to achieve the desired shape, efficiently producing cylindrical and tapered parts with high accuracy and consistency.
- CNC routers: Designed for precision, CNC routers can cut and shape materials such as wood, plastic, and metal, enabling complex 3D designs for industries that require detailed patterns and high precision.
- EDM machines: Advanced cutting methods include sinker EDM and wire EDM. While sinker EDM uses an electrode to perform controlled hot erosion in a dielectric fluid, wire EDM uses a thin wire electrode to make intricate cuts.
CNC Machining Parameters and Xtproto’s Machining Capabilities
CNC machining is well known for its high accuracy and flexibility. The final machining result depends on the parameters set in the CNC program, such as cutting speed, tool movement, and machining depth.
At Xtproto, our CNC milling machines can process large parts with a maximum size of 4000 × 1500 × 600 mm (157 × 59 × 24 in). This provides a much larger working area compared to most 3D printers, making CNC machining suitable for both small and large components.
For CNC turning, we can machine parts with diameters of up to 200 mm (7.9 in), covering a wide range of cylindrical components. Our machines are capable of achieving high precision, with tolerances as tight as ±0.001 in (±0.025 mm). This means the size difference is smaller than the thickness of a human hair.
Xtproto also offers fast production times. Standard orders are typically completed within 5 working days, and simple parts can be delivered in as little as 1 working day. We are committed to providing reliable, accurate, and efficient CNC machining services to meet different manufacturing needs.
3D Printing Can Overcome Some Design Limits of CNC Machining
When designing parts with very complex shapes, it is important to understand the limitations of CNC machining. CNC machining works by cutting material away using tools, and this naturally places some limits on the shapes that can be made. In comparison, 3D printing builds parts layer by layer, which allows it to create complex geometries without significantly increasing cost.
With CNC machining, higher part complexity usually means higher cost. This is because complex designs often require additional setups, special tools, or longer machining time. One of the main limitations comes from the shape of cutting tools. Most cutting tools are round, which makes it difficult to create sharp internal corners or deep internal features.
Another important factor is tool accessibility. A standard three-axis CNC machine can only machine features that the tool can reach from one direction, usually from the top. More advanced five-axis machines allow the tool or the part to rotate, making it possible to reach more angles and machine more complex features. However, five-axis machining is more expensive and not always necessary.
Thin-walled parts are also challenging for CNC machining. Because the cutting process applies force to the material, thin walls may vibrate, deform, or even break during machining. These issues are less common in 3D printing, which applies very little force during the build process.
By understanding these limitations during the design stage, engineers can decide whether CNC machining or 3D printing is the better choice, ensuring that the final part is both manufacturable and high quality.
Why Xtproto Is the Right Manufacturing Partner for Your CNC Projects
For small and medium-sized businesses, meeting CNC manufacturing needs can be resource-intensive and requires expertise in both part machining and CNC certification. To meet these challenges, partnering with a professional CNC machining provider like Xtproto has become a common industry practice. Xtproto is the ideal manufacturing partner to provide top-notch CNC machining services. The company is headquartered in China, a global manufacturing hub, and has an excellent track record. Able to achieve tolerances as precise as 0.01 mm, Xtproto’s team of experts offers a range of services including CNC Turning Services, CNC Milling Services, Sheet Metal Production Services.
For small and medium-sized businesses, CNC manufacturing can be challenging. It often requires specialized equipment, skilled technicians, and strict quality standards. Because of this, many companies choose to work with professional CNC machining providers instead of building everything in-house.
Xtproto is a reliable manufacturing partner that offers professional CNC machining services. Based in China, one of the world’s leading manufacturing centers, Xtproto has extensive experience in producing high-quality machined parts. Our team is capable of achieving tight tolerances of up to 0.01 mm, and we provide a wide range of services, including CNC turning, CNC milling, and sheet metal fabrication.
Quality is a top priority at Xtproto. We are ISO 9001 certified and use well-established quality control processes to ensure that every part meets customer requirements. From prototyping to full-scale production, our focus on precision, consistency, and reliability makes us a trusted choice for many CNC machining projects.
Start your CNC project with Xtproto today. With advanced manufacturing technology and experienced engineers, we help turn your ideas into high-quality finished parts.
Conclusion
CNC machining is a cornerstone of modern industry, sparking curiosity among those in and outside the industry. It is a key driver of the industrial age and will play a major role in the future. The rise of smart factories and Industry 4.0 depends on CNC machining capabilities. This technology combines manual machining with digital control, ensuring unparalleled precision and consistency. Although this manufacturing technology has some limitations, its advantages far outweigh the challenges. As the technology develops, current issues are expected to be resolved, further enhancing its impact. Want to experience top-notch CNC machining results? Contact Xtproto today to explore the excellence of advanced CNC solutions!
