The Basics of CNC Machining Explained from Concept to Manufacturing
Manufacturers often face problems such as high production costs, poor quality control, and slow delivery. CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machining solves these problems with its precision, efficiency, and scalability. Compared to operator-controlled manual machining, CNC machining automates operations such as drilling, cutting, and forming with an accuracy of ±0.001 mm.CNC technology has continued to evolve over the years to become more efficient and smarter. This is a guide to CNC machining technology in the manufacturing industry to help companies choose the right machines and technology. Let’s continue reading the basics of CNC machining technology terminology, processes, and everything in between!
What is CNC machining?
CNC machining is a digital manufacturing process that uses computers to control machines and create parts from solid materials. Instead of being operated manually, the machines follow programmed instructions to cut, drill, and shape materials into the required form.
Compared with traditional machining methods, CNC machining is faster, more accurate, and delivers consistent results. For this reason, it is widely used in custom part manufacturing and across many industries to produce prototypes, functional components, and production parts.

How Does CNC Machining Work?
CNC machining works by using computers to control the movement of machine tools. A digital design defines the shape of the part, and the machine follows programmed instructions to move cutting tools with high precision.
Instead of relying on manual operation, the computer controls factors such as tool position and movement, allowing material to be removed accurately and consistently. This computer-controlled approach is what enables CNC machining to produce complex parts with reliable and repeatable results.
Basic Workflow of CNC Machining Projects
To better understand how CNC machining works in practice, it helps to look at the basic workflow of a typical machining project. Although the details may vary, the process generally follows these steps.
1. Create a digital design
The process begins with a digital design of the part, usually created in 2D or 3D using design software. This design defines the shape, size, and basic features of the part to be manufactured.
2. Convert the design into machine instructions
The digital design is then translated into instructions that the CNC machine can understand. These instructions guide how the machine moves and how the material will be cut or shaped.
3. Set up the CNC machine
Before machining starts, the raw material is securely fixed in place, and the appropriate cutting tools are selected. Proper setup helps ensure accuracy during the machining process.
4. Execute the machining process
Once everything is prepared, the CNC machine runs automatically according to the instructions. It removes material step by step until the final part is formed.
5. Inspect the finished part
After machining, the part is checked to confirm it matches the original design. This step ensures consistency and quality before the part is used or delivered.
Main Components of CNC Machining Equipment
CNC machining equipment is made up of several key components that work together to produce precise and repeatable parts. Each component plays a specific role in ensuring the machining process runs accurately, efficiently, and within tight tolerances. Below are the main components involved in a typical CNC machining system.
CNC Machine
The CNC machine is the main piece of hardware that performs the actual machining work. It carries out operations such as cutting, drilling, milling, and shaping based on programmed instructions. Depending on the machine type, it can move along different axes to create simple or complex part geometries.
Controller
The controller acts as the brain of the CNC machine. It receives instructions from the CNC program and converts them into precise machine movements. By controlling speed, position, and tool paths, the controller ensures consistent accuracy throughout the machining process.
CNC Software
CNC software is used to design parts and prepare them for manufacturing. It helps create digital models, generate machining instructions, and define how each operation should be performed. The software ensures that the machining process follows the design requirements step by step.
Cutting Tools
Cutting tools are responsible for removing material from the workpiece. Different tools are used for different tasks, such as drilling holes, milling surfaces, or turning round features. The choice of cutting tool depends on the material being machined and the desired part geometry.
Main Types of CNC Machines
CNC machines can be classified into several main types based on the kind of machining operations they perform. Each type of CNC machine is designed for specific tasks and materials, helping manufacturers produce parts with different shapes, tolerances, and surface finishes
CNC Milling Machine
CNC milling machines are used for milling operations, where a rotating cutting tool removes material from a stationary workpiece. They are suitable for producing flat surfaces, slots, holes, and complex 3D shapes. Most milling machines operate on three axes (X, Y, and Z), while more advanced models use four or five axes to machine complex parts. CNC milling machines are widely used in prototyping, automotive components, and medical devices.
CNC Lathes (Turning Centers)
CNC lathes are designed for turning operations. In this process, the workpiece rotates while a cutting tool shapes it into cylindrical or round parts. CNC lathes offer high precision and repeatability compared to manual lathes, making them ideal for manufacturing shafts, bolts, bushings, pipe fittings, and aerospace components.
CNC Routers
CNC routers are mainly used for cutting and engraving softer materials such as wood, plastics, foam, and light metals. They operate at high speeds and are well suited for large-format parts. CNC routers are commonly used in furniture manufacturing, signage, cabinet making, and architectural modeling.
CNC Grinding Machines
CNC grinding machines use grinding wheels to remove very small amounts of material and achieve extremely smooth surfaces. These machines are primarily used for finishing operations that require tight tolerances and high surface quality. Common applications include tool sharpening, gear manufacturing, and precision aerospace components.
CNC Electrical Discharge Machining Machines (EDM)
CNC EDM machines remove material using controlled electrical discharges instead of physical cutting tools. This non-contact machining method is ideal for hardened metals and complex geometries that are difficult to machine with traditional methods. CNC EDM is widely used for producing molds, dies, turbine blades, and other high-precision metal components.
CNC Programming and Design
After understanding the main types of CNC machines, the next key question is how these machines are actually instructed to make a part. CNC programming and design are what turn an idea into a physical part. While CNC machines perform the actual cutting, it is the program that tells the machine exactly how to move, which tools to use, and how fast each operation should run. This process mainly involves CAD design, CAM programming, and CNC control codes.
How CNC Programming Works
CNC programming usually begins with a digital part design created using CAD (Computer-Aided Design) software. The CAD model defines the part’s shape, dimensions, and features. After the design is finalized, it is imported into CAM (Computer-Aided Manufacturing) software.
CAM software converts the design into a CNC program that the machine can understand. During this process, tool paths, cutting speeds, feed rates, and machining sequences are generated. The finished program is then sent to the CNC machine, which follows these instructions to produce the part. In some cases, operators can also make small adjustments directly on the machine to fine-tune accuracy or improve efficiency.
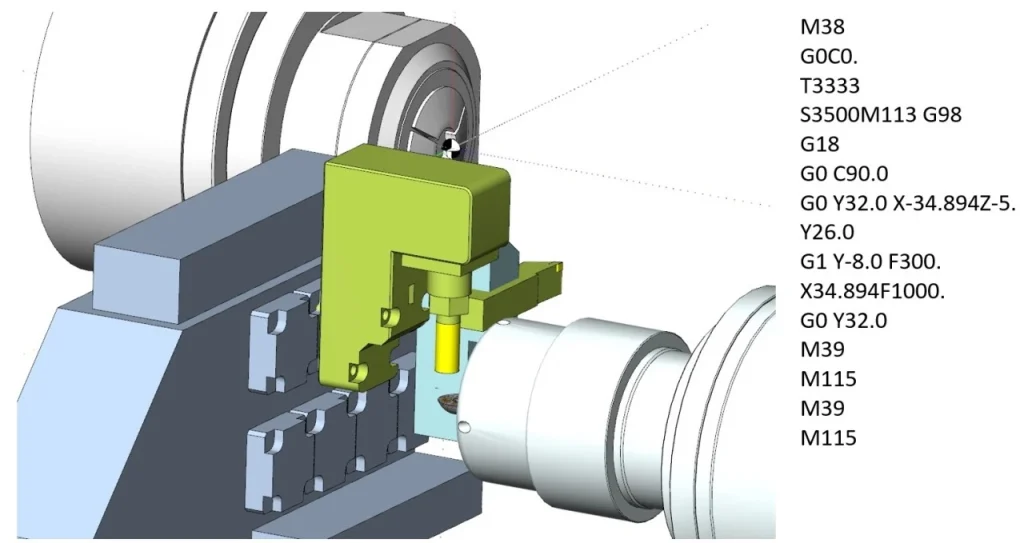
G-code and M-code
CNC machines are controlled using two main types of programming codes: G-codes and M-codes.
G-code (Geometric Code) controls the movement of the machine. It tells the machine where to move, how fast to move, and which path to follow. For example, G-code commands are used for linear movement, circular motion, and positioning during cutting operations.
M-code (Miscellaneous Code) controls auxiliary machine functions that are not related to movement. These include actions such as starting or stopping the spindle, activating coolant flow, and changing tools during machining.
Together, G-codes and M-codes ensure that machining operations are performed accurately and consistently.
Importance of CAM Software
CAM software plays a key role in improving efficiency and accuracy in CNC machining. It helps reduce human error by automatically generating optimized tool paths and machining instructions. CAM systems can also simulate machining operations before production, allowing potential issues to be identified and corrected in advance.
By optimizing machining processes and reducing material waste, CAM software enables CNC machines to achieve the high precision required in industries such as automotive, aerospace, and medical manufacturing.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CNC Machining
CNC machining is widely used for producing high-precision custom parts. However, like any manufacturing process, it has both strengths and limitations. Understanding these pros and cons helps you decide whether CNC machining is the right solution for your project.
Advantages of CNC Machining
High precision and accuracy
CNC machining can achieve very tight tolerances, making it ideal for parts that require consistent dimensions and reliable performance.
Excellent repeatability for batch production
Once the program is set, the same part can be produced repeatedly with stable quality, which is especially important for low- to medium-volume production.
Wide range of material options
CNC machining works with metals, plastics, and engineering materials, giving designers flexibility across different industries.
Fast and efficient production
Automated operation reduces manual labor and shortens lead times, helping manufacturers deliver parts faster.
Capable of complex geometries
Multi-axis CNC machines can produce complex shapes that are difficult to achieve with traditional machining.
Disadvantages of CNC Machining
Higher upfront cost
CNC machines, tooling, and programming require an initial investment, which may not be ideal for very simple or one-off parts.
Programming and setup are required
Skilled programming is necessary to ensure accuracy, which can add time at the beginning of a project.
Material waste from subtractive processing
Since material is removed from a solid block, CNC machining may generate more waste compared to additive manufacturing methods.
Common Materials Used in CNC Machining
CNC machining supports a wide range of materials, allowing manufacturers to produce parts with different strength, weight, and performance requirements.
Metals
- Aluminum – Lightweight, easy to machine, and cost-effective. Widely used in aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
- Steel & Stainless Steel – High strength and durability, suitable for industrial, structural, and medical applications.
- Brass & Copper – Good electrical conductivity and machinability, commonly used for electrical components.

Plastics
- ABS & Nylon – Strong, impact-resistant, ideal for functional prototypes and mechanical parts.
- POM (Delrin) – Low friction and high dimensional stability for precision plastic components.
- Acrylic (PMMA) – Transparent material often used for display and visual parts.
Advanced Materials
- Titanium – High strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance, commonly used in aerospace and medical industries.
- Composites – Used for lightweight and high-performance applications.
Applications of CNC Machining
CNC machining is widely used across many industries due to its high precision, consistency, and flexibility. It is especially suitable for producing complex and custom parts with tight tolerances.
- Aerospace
Used for manufacturing high-precision components such as brackets, housings, and structural parts that require tight tolerances and lightweight materials. - Automotive
Commonly applied in prototyping, engine components, fixtures, and low- to medium-volume production parts. - Medical
CNC machining enables the production of medical devices and components that require high accuracy, smooth surface finishes, and strict quality standards. - Electronics
Used to produce enclosures, connectors, and precision parts for electronic devices. - Industrial Equipment
Widely used for custom machinery parts, tools, and mechanical components across various industries.
Future of CNC Machining
CNC machining is evolving toward greater automation and intelligence. With advancements such as AI-driven systems, multi-axis machining, and hybrid manufacturing that combines CNC machining with 3D printing, manufacturers can achieve faster prototyping, higher precision, and more efficient production in the future.
Conclusion
CNC machining plays a vital role in modern manufacturing, offering high precision, efficiency, and flexibility across industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical. As automation, artificial intelligence, and IoT technologies continue to advance, CNC machining is becoming even more reliable, scalable, and cost-effective.
When selecting a CNC machining partner, factors such as material capability, part complexity, and production volume are critical. Xtproto provides reliable CNC machining services backed by advanced equipment, experienced engineers, and strict quality control. From rapid prototyping to low- and high-volume production, we deliver accurate and efficient machining solutions tailored to your needs.
If you are looking for a trusted CNC machining manufacturer, Xtproto is ready to support your project.
👉 Contact Xtproto to get started.
FAQ
What are the basics of CNC machining?
The basics of CNC machining include using computer-controlled machines to remove material from a workpiece based on a digital design, ensuring high precision, repeatability, and efficiency.
What is CNC for beginners?
For beginners, CNC refers to computer-controlled machines that follow programmed instructions to produce accurate and consistent parts from materials like metal or plastic.
What are the major parts of a CNC machine?
The main parts of a CNC machine include the machine tool, controller, software system, cutting tools, spindle, worktable, and drive system.
